How to select a CC2530 board
Ebay and Aliexpress offer several boards with the CC2530 chip (keyword: CC2530). You may select any board, but use the following criteria:
- The board must have the CC2530F256 chip (fig. 3). The key number here is 256 and it means 256 KB of flash memory. Most firmware was compiled for 256K memory.
- The board may have many pins or contacts. If you do not have a soldering iron then select a board with headers. I would suggest to select a board where each pin has the corresponding label. The label may slightly different on different boards: P0.2, P02, P0_2 are the same pin. The board must have at least the following pins:
- Po.2, Po.3, P2.0 – used for a UART interface. If you plan to use this board instead CC2531 and connect to your SBC like Raspberry Pi, then you need these pins. If you’ll upload a router firmware to this board then these pins are optional.
- P2.1, P2.2, RST – used for uploading firmware.
- GND – ground.
- Power source (VCC) – it may be 3.3V, 5V or both. This pin can be marked by VCC only. Internally, the CC2530 chip uses the 3.3V voltage, but a manufacturer may add a voltage regulator on the board and you may use any supported voltage (3.3V or 5V, no difference). Please, read a description for this board carefully about the voltage.
- The board may include an additional small chip (fig.5). Most likely, this is a wireless signal amplifier. Usually these boards contain “Long range”, “RF front-end”, “RF amplifier”, “CC2591”, “RXF2401” in a description. These boards require a special firmware. I would suggest to select this board if you really have a firmware for this combination of the main chip (CC2530) and the RF front-end chip.
- The board may contain an antenna on-board (fig.2, 3, 6) or a connector for an external antenna (fig. 1, 3, 4, 5). The board with an external antenna will work better in most cases.
- Some boards may have a metallic shield over the main chip and/or the RF front-end. This shield protects the board from radio noises (good). But I would suggest to buy this board from a trusted vendors only because you cannot be sure about chips under this cover.
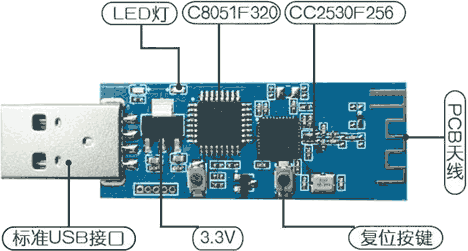
- Rare CC2530 based boards may include an USB interface (fig. 6). CC2530 does not have native USB support apart from CC2531. Therefore a manufacturer adds an additional chip on the board. The additional chip implements the USB interface and the CC debugger. Therefore you can upload a firmware to this board without a special debugger (CC debugger or SmartRF04EB). Therefore it holds small space on your work table. It can be useful for developers. If you need only one CC2530 or CC2531 for a coordinator role you may save money. Please, read a description for a board carefully because this USB interface and chip may be used for another purpose. Therefore I cannot recommend this board for beginners.
 https://ptvo.info/wp-content/uploads/2018/05/cc2530_2_2-287x300.png 287w" sizes="(max-width: 203px) 100vw, 203px" style="box-sizing: border-box; border: 0px; display: block; margin: 0px auto 5px; max-width: 100%; height: auto; border-radius: 4px;"> https://ptvo.info/wp-content/uploads/2018/05/cc2530_2_2-287x300.png 287w" sizes="(max-width: 203px) 100vw, 203px" style="box-sizing: border-box; border: 0px; display: block; margin: 0px auto 5px; max-width: 100%; height: auto; border-radius: 4px;"> |
Fig. 1 The compact board with an external antenna |
 https://ptvo.info/wp-content/uploads/2018/06/CC2530-2-300x158.png 300w, https://ptvo.info/wp-content/uploads/2018/06/CC2530-2-600x316.png 600w, https://ptvo.info/wp-content/uploads/2018/06/CC2530-2-680x358.png 680w" sizes="(max-width: 245px) 100vw, 245px" style="box-sizing: border-box; border: 0px; display: block; margin: 0px auto 5px; max-width: 100%; height: auto; border-radius: 4px;"> https://ptvo.info/wp-content/uploads/2018/06/CC2530-2-300x158.png 300w, https://ptvo.info/wp-content/uploads/2018/06/CC2530-2-600x316.png 600w, https://ptvo.info/wp-content/uploads/2018/06/CC2530-2-680x358.png 680w" sizes="(max-width: 245px) 100vw, 245px" style="box-sizing: border-box; border: 0px; display: block; margin: 0px auto 5px; max-width: 100%; height: auto; border-radius: 4px;"> |
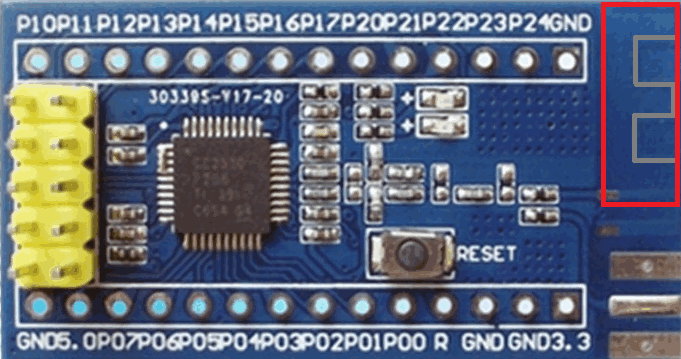
Fig. 2 The board with the internal antenna, place for an external antenna connector and a debug interface header (compatible with the CC debugger cable, the dupont cable is not required) |
 https://ptvo.info/wp-content/uploads/2018/06/CC2530-1-300x249.png 300w" sizes="(max-width: 151px) 100vw, 151px" style="box-sizing: border-box; border: 0px; display: block; margin: 0px auto 5px; max-width: 100%; height: auto; border-radius: 4px;"> https://ptvo.info/wp-content/uploads/2018/06/CC2530-1-300x249.png 300w" sizes="(max-width: 151px) 100vw, 151px" style="box-sizing: border-box; border: 0px; display: block; margin: 0px auto 5px; max-width: 100%; height: auto; border-radius: 4px;"> |
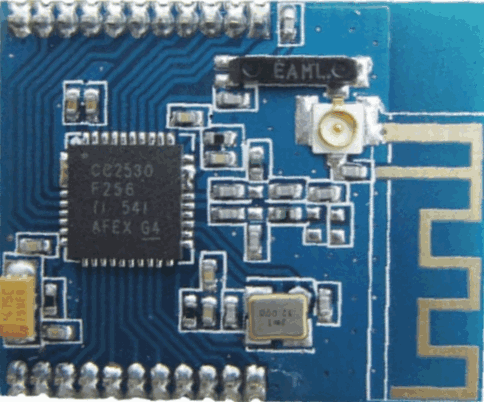
Fig. 3 The compact board with the internal ceramic antenna and an external antenna connector |
 https://ptvo.info/wp-content/uploads/2018/06/CC2530-3-300x177.png 300w" sizes="(max-width: 226px) 100vw, 226px" style="box-sizing: border-box; border: 0px; display: block; margin: 0px auto 5px; max-width: 100%; height: auto; border-radius: 4px;"> https://ptvo.info/wp-content/uploads/2018/06/CC2530-3-300x177.png 300w" sizes="(max-width: 226px) 100vw, 226px" style="box-sizing: border-box; border: 0px; display: block; margin: 0px auto 5px; max-width: 100%; height: auto; border-radius: 4px;"> |
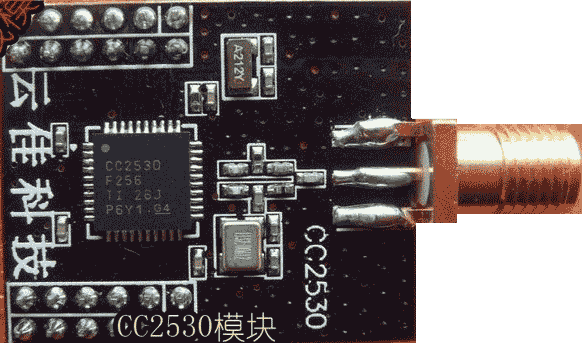
Fig. 4 The compact board with an external antenna. Black design. |
 https://ptvo.info/wp-content/uploads/2018/06/CC2530-PA-4-300x231.png 300w" sizes="(max-width: 192px) 100vw, 192px" style="box-sizing: border-box; border: 0px; display: block; margin: 0px auto 5px; max-width: 100%; height: auto; border-radius: 4px;"> https://ptvo.info/wp-content/uploads/2018/06/CC2530-PA-4-300x231.png 300w" sizes="(max-width: 192px) 100vw, 192px" style="box-sizing: border-box; border: 0px; display: block; margin: 0px auto 5px; max-width: 100%; height: auto; border-radius: 4px;"> |
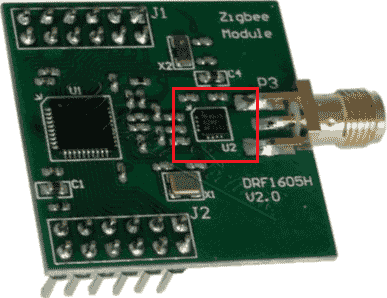
Fig. 5 The CC2530 board with the RF front-end |
 https://ptvo.info/wp-content/uploads/2018/06/CC2530-5-300x161.png 300w" sizes="(max-width: 272px) 100vw, 272px" style="box-sizing: border-box; border: 0px; display: block; margin: 0px auto 5px; max-width: 100%; height: auto; border-radius: 4px;"> https://ptvo.info/wp-content/uploads/2018/06/CC2530-5-300x161.png 300w" sizes="(max-width: 272px) 100vw, 272px" style="box-sizing: border-box; border: 0px; display: block; margin: 0px auto 5px; max-width: 100%; height: auto; border-radius: 4px;"> |
Fig. 6 The CC2530 board with a USB connector and the additional 8051 chip |
Pre-requisites
Here is an example for the most simple case when all pins are soldered on the board and have labels (fig. 1).
- The CC2530 board.
- The dupont cable (5 wires, female – female).
- The CC-debugger or SmartRF04EB (look very similar).
- The USB cable between the debugger and your computer (it usually comes with the debugger, USB-A <-> USB-mini).
- Computer with Windows.
- Flash Programmer V1 (V2 does not work).
How to connect CC2530 to the debugger
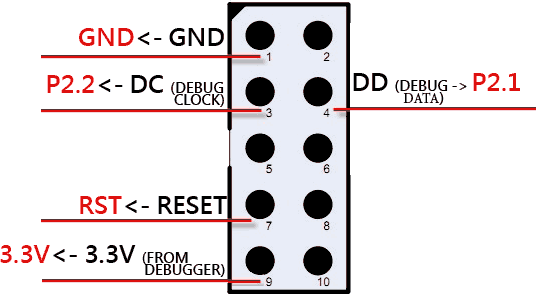
This is simple. Use the dupont cable and connect pins on the debugger’s connector to the corresponding pin on your board.
Note: if CC-debugger cannot detect your board, additionally try to connect the pin #2 to 3.3V.
 https://ptvo.info/wp-content/uploads/2018/06/smartrf04eb-pinout-300x165.png 300w" sizes="(max-width: 536px) 100vw, 536px" style="box-sizing: border-box; border: 0px; display: block; margin: 0px auto 5px; max-width: 100%; height: auto; border-radius: 4px;">
https://ptvo.info/wp-content/uploads/2018/06/smartrf04eb-pinout-300x165.png 300w" sizes="(max-width: 536px) 100vw, 536px" style="box-sizing: border-box; border: 0px; display: block; margin: 0px auto 5px; max-width: 100%; height: auto; border-radius: 4px;">
 https://ptvo.info/wp-content/uploads/2018/06/smartrf04eb_cc2530-215x300.jpg 215w" sizes="(max-width: 265px) 100vw, 265px" style="box-sizing: border-box; border: 0px; display: block; margin: 0px auto 5px; max-width: 100%; height: auto; border-radius: 4px;">
https://ptvo.info/wp-content/uploads/2018/06/smartrf04eb_cc2530-215x300.jpg 215w" sizes="(max-width: 265px) 100vw, 265px" style="box-sizing: border-box; border: 0px; display: block; margin: 0px auto 5px; max-width: 100%; height: auto; border-radius: 4px;">
The board from fig. 2 is compatible with a flat white cable usually shipped with CC-debugger or SmartRF04EB. This flat cable can be connected to the yellow header (the red wire should be connected to pin #1 of this header).
 https://ptvo.info/wp-content/uploads/2018/06/smartrf04eb-150x150.jpg 150w" sizes="(max-width: 225px) 100vw, 225px" style="box-sizing: border-box; border: 0px; display: block; margin: 0px auto 5px; max-width: 100%; height: auto; border-radius: 4px;">
https://ptvo.info/wp-content/uploads/2018/06/smartrf04eb-150x150.jpg 150w" sizes="(max-width: 225px) 100vw, 225px" style="box-sizing: border-box; border: 0px; display: block; margin: 0px auto 5px; max-width: 100%; height: auto; border-radius: 4px;">
Note: if your board has the 5V power pin only then you must connect an external power source (5V and GND) to the corresponding pins on your board instead of 3.3V from the debugger. GND of the debugger and the power source must be connected at the same time.
How to connect a CC-debugger to your computer
Connect your debugger to a USB port on your computer using a standard USB cable. A new USB device should appear in Devices Manager on your computer. If you’ve installed Texas Instruments Flash Programmer before, the drivers for the new USB device will be installed automatically. You should see something like “SmartRF04EB” or “CC-debugger” in Devices Manager.
How to select a right firmware
Here are examples for general usage cases. All these examples may have exceptions.
- Select a firmware for the right chip: CC2530 in our case.
- If your board has a RF front-end chip then you must select a firmware for combination of the main chip and the RF chip (for example CC2530 + RXF2401). For example, CC2530ZNP-Pro-Secure_LinkKeyJoin_RXF2401.hex
- Select a firmware for your Zigbee network. Devices with different network parameters are incompatible (they cannot communicate). Each Zignbee network has the following key parameters:
- Network Id (PanId).
- Security key.
- Radio channel number. This requirement is not strict. Many Zigbee devices may scan channels and find the correct channel number. But some Zigbee devices work with the pre-defined channel number only.
- Select a firmware for the device type you want to get from the CC2530 board:
- Coordinator: it should be connected to a computer or SBC (Raspberry Pi, BananaPi, OrangePi, etc), because in most cases it operates under control of a computer. The firmware file name or a description may contain keywords: “coordinator”, “ZNP”. For example, CC2530ZNP-Pro-Secure_LinkKeyJoin.hex. The ZNP firmware is universal, because it operates under control of a computer and it may configure the board as necessary, probably for any Zigbee network.
- Router: it works independently (not linked to a computer) and extends coverage of your Zigbee network. For example, CC2530-router.hex.
You may download my firmware for a Xiaomi coordinator and router here.
How to flash (upload) firmware
Ok. You’ve connected the debugger and the board.
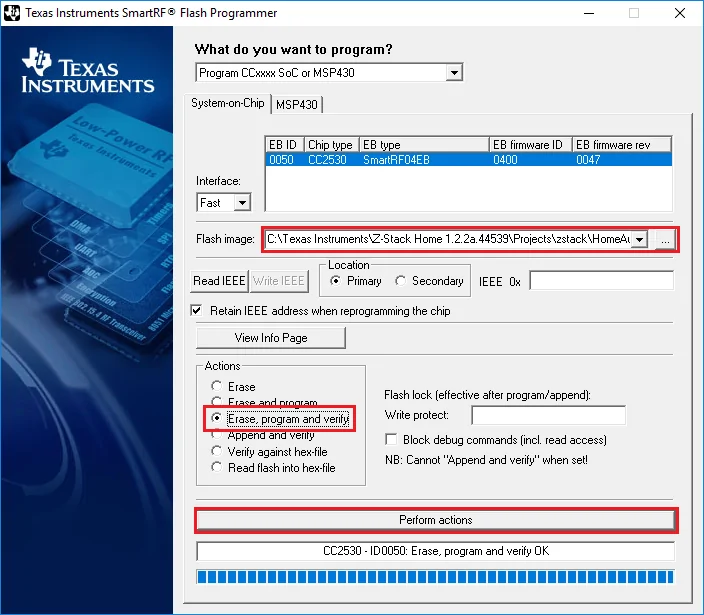
- Start Flash Programmer. Your debugger should be in the list. If the debugger does not appear there try to press the “Reset” button on the debugger.
- Select a firmware file using the “…” button.
- Select the following options.
- Click the “Perform actions” button.
 https://ptvo.info/wp-content/uploads/2018/06/flash-programmer-v1-300x262.png 300w, https://ptvo.info/wp-content/uploads/2018/06/flash-programmer-v1-600x524.png 600w, https://ptvo.info/wp-content/uploads/2018/06/flash-programmer-v1-680x594.png 680w" sizes="(max-width: 704px) 100vw, 704px" style="box-sizing: border-box; border: 0px; display: block; margin: 0px auto 5px; max-width: 100%; height: auto; border-radius: 4px;">
https://ptvo.info/wp-content/uploads/2018/06/flash-programmer-v1-300x262.png 300w, https://ptvo.info/wp-content/uploads/2018/06/flash-programmer-v1-600x524.png 600w, https://ptvo.info/wp-content/uploads/2018/06/flash-programmer-v1-680x594.png 680w" sizes="(max-width: 704px) 100vw, 704px" style="box-sizing: border-box; border: 0px; display: block; margin: 0px auto 5px; max-width: 100%; height: auto; border-radius: 4px;">